C/2017 E3 PANSTARRS
more info
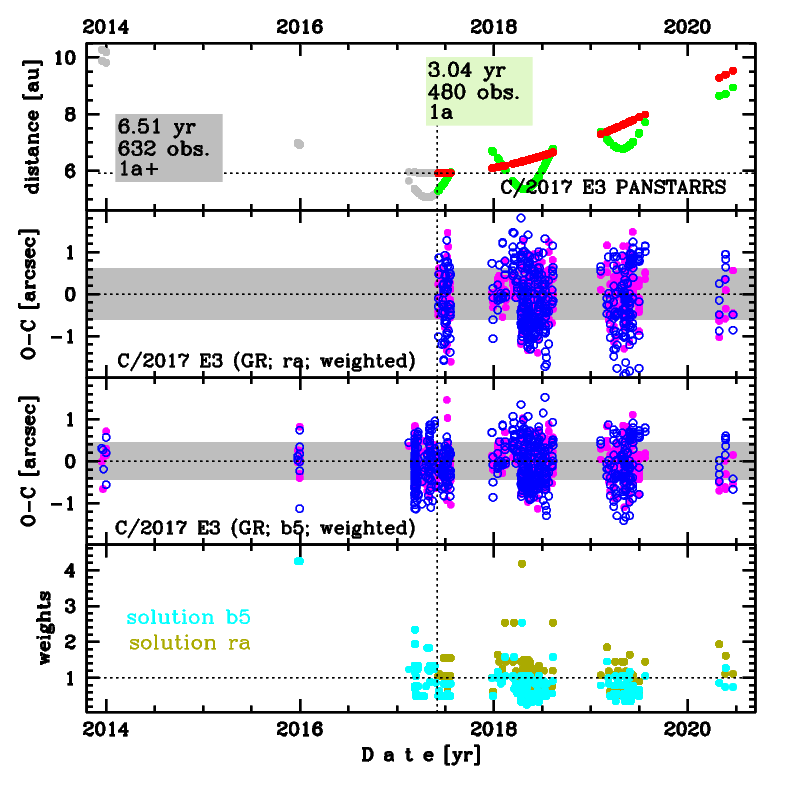
Comet C/2017 E3 was discovered on 7 March 2017 with Pan-STARRS 1 telescope (Haleakala), that is about 3 months before its perihelion passage. Later, it was found on a series of earlier images going back to December 2013. This comet was observed until 20 June 2020.
Comet had its closest approach to the Earth on 24 April 2017 (3.480 au), about 1.5 month after discovery and more than a month before its perihelion passage.
Solutions given here are based on data spanning over 6.51 yr in a range of heliocentric distances: 10.28 au 5.915 au (perihelion) 9.53 au (July 2023).
This Oort spike comet suffers moderate planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; these perturbations lead to escape the comet from the planetary zone on a hyperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbits).
See also Królikowska and Dones 2023.
| solution description | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of observations | 480 | |
| data interval | 2017 06 05 – 2020 06 20 | |
| data arc selection | data generally limited to post-perihelion (POS) | |
| range of heliocentric distances | 5.9 au – 9.53au | |
| detectability of NG effects in the comet's motion | NG effects not determinable | |
| type of model of motion | GR - gravitational orbit | |
| data weighting | YES | |
| number of residuals | 943 | |
| RMS [arcseconds] | 0.61 | |
| orbit quality class | 1a | |
| orbital elements (heliocentric ecliptic J2000) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 2017 06 16 | |
| perihelion date | 2017 05 31.57540002 | ± 0.00142131 |
| perihelion distance [au] | 5.91525793 | ± 0.00000765 |
| eccentricity | 1.00498658 | ± 0.00000644 |
| argument of perihelion [°] | 333.663842 | ± 0.000137 |
| ascending node [°] | 220.758578 | ± 0.000008 |
| inclination [°] | 70.665055 | ± 0.000021 |
| reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | -843.00 | ± 1.09 |