C/2015 LC2 PANSTARRS
more info
Comet C/2015 LC2 was discovered on 7 June 2015 with Pan-STARRS 1 telescope (Haleakala), that is about a month
after its perihelion passage.This comet was observed until 17 August 2018.
Comet had its closest approach to the Earth on 8 May 2015 (4.939 au), a week after its perihelion passage.
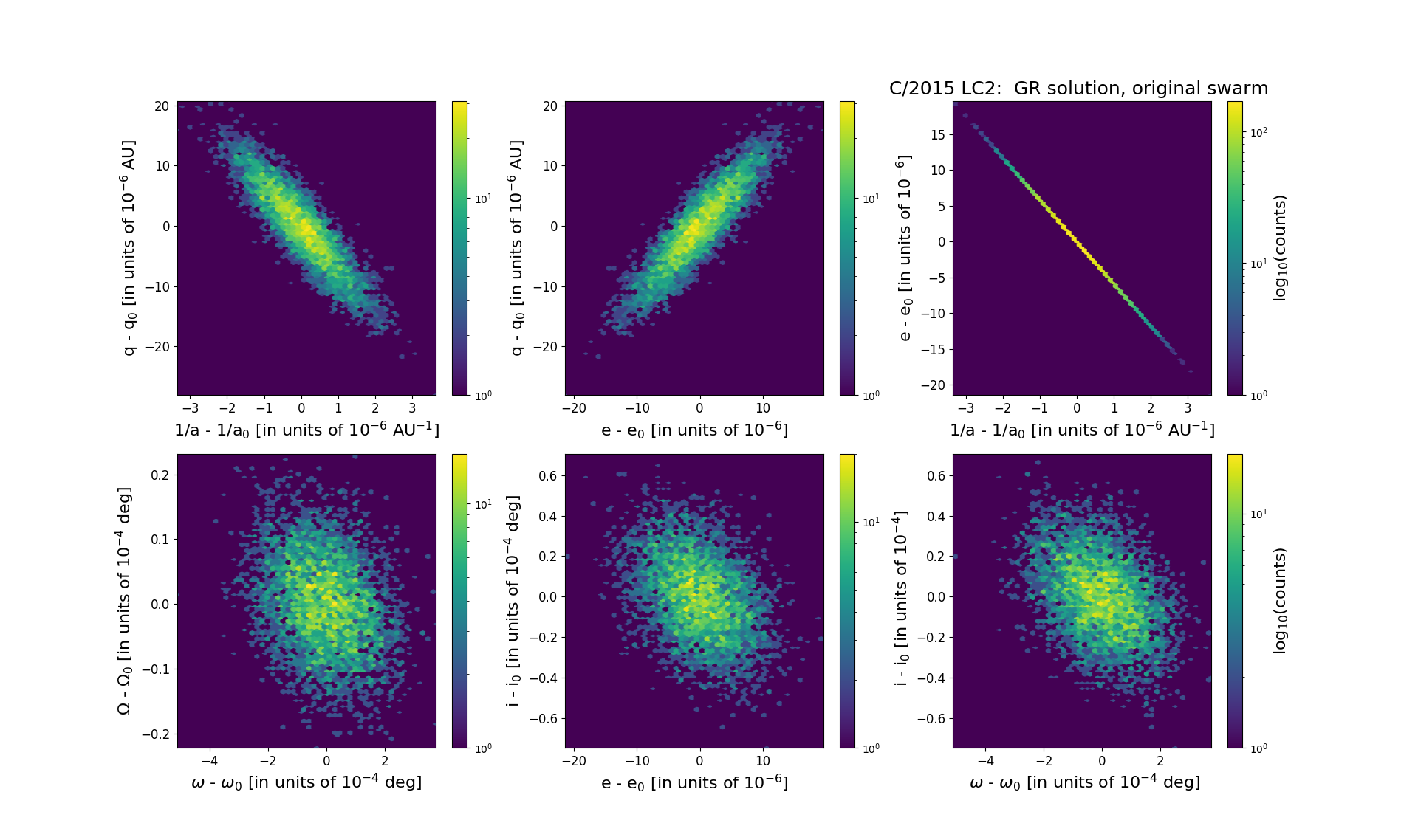
Solution given here is based on data spanning over 2.78 yr in a range of heliocentric distances from 5.90 au to 9.97 au.
This comet suffers insignificant planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; have original semimajor axis shorter than 10000 au.
Comet had its closest approach to the Earth on 8 May 2015 (4.939 au), a week after its perihelion passage.
Solution given here is based on data spanning over 2.78 yr in a range of heliocentric distances from 5.90 au to 9.97 au.
This comet suffers insignificant planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; have original semimajor axis shorter than 10000 au.
| solution description | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of observations | 439 | |
| data interval | 2015 06 07 – 2018 08 17 | |
| data type | observed only after perihelion (POST) | |
| data arc selection | entire data set (STD) | |
| range of heliocentric distances | 5.9 au – 9.97au | |
| detectability of NG effects in the comet's motion | NG effects not determinable | |
| type of model of motion | GR - gravitational orbit | |
| data weighting | YES | |
| number of residuals | 876 | |
| RMS [arcseconds] | 0.45 | |
| orbit quality class | 1a+ | |
| orbital elements (barycentric ecliptic J2000) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 1705 06 12 | |
| perihelion date | 2015 05 02.86770248 | ± 0.00114650 |
| perihelion distance [au] | 5.88686907 | ± 0.00000637 |
| eccentricity | 0.99843174 | ± 0.00000513 |
| argument of perihelion [°] | 341.961693 | ± 0.000114 |
| ascending node [°] | 223.584994 | ± 0.000007 |
| inclination [°] | 93.74534 | ± 0.000019 |
| reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | 266.40 | ± 0.87 |
| file containing 5001 VCs swarm |
|---|
| 2015lcb5.bmi |