C/1885 X1 Fabry
more info
C/1885 X1 was discovered on 1 December 1885 by Louis Fabry (Paris, France), about 5 months before its perihelion passage, and the comet was last seen on 30 July 1886 [Kronk, Cometography: Volume 2].
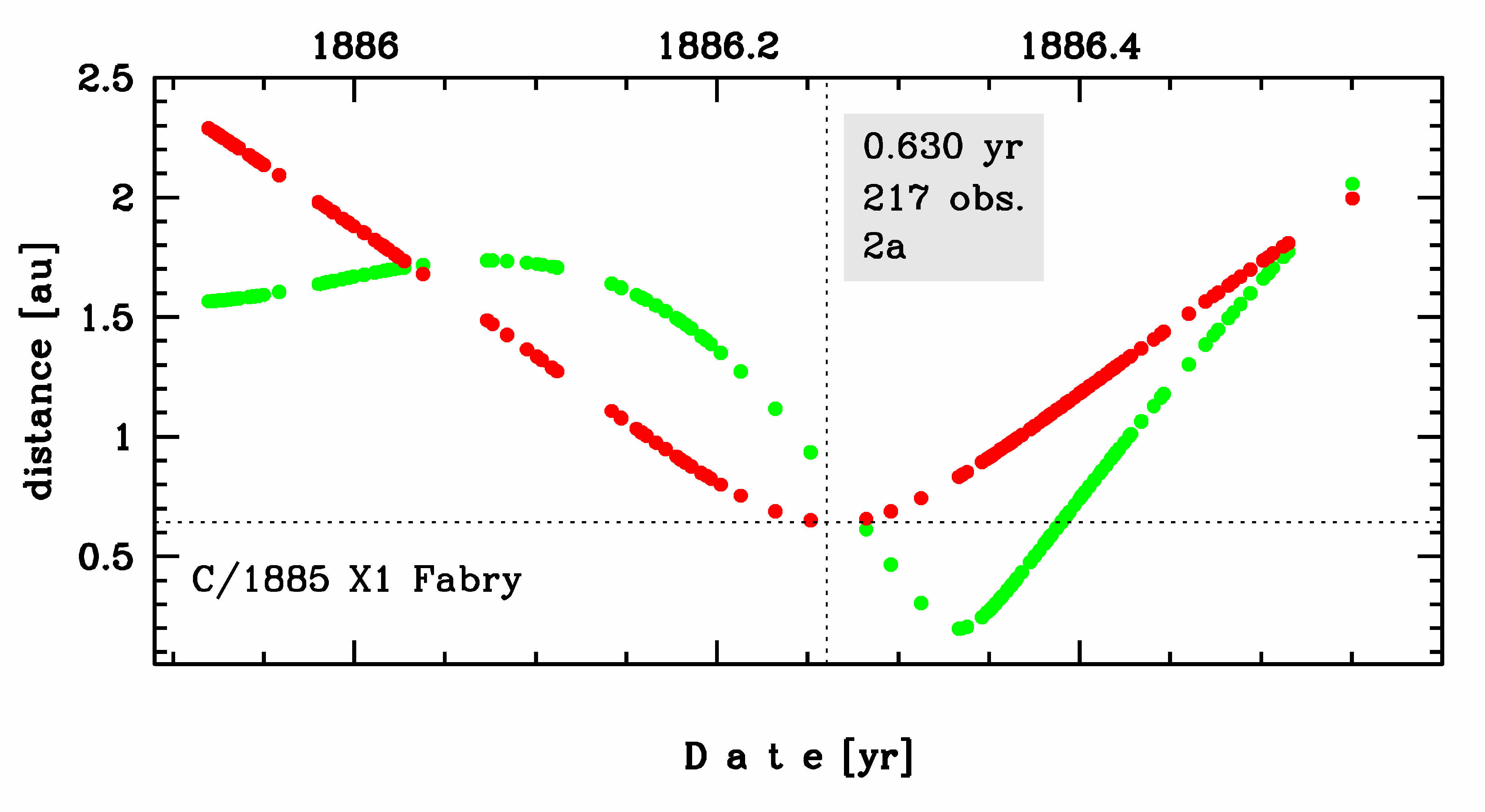
This comet made its closest approach to the Earth on 1 May 1886 (0.198 au), that is less than two weeks before perihelion passage.
Solutions given here are based on data spanning over 0.630 yr in a range of heliocentric distances from 2.29 au through perihelion (0.642 au) to 2.00 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers small planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; these perturbations lead to escape the comet from the planetary zone on a hyperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbits).
C/1885 X1 was in the original sample of 19 comets used by Oort for his hypothesis on LPCs; however, according to presented here statistics for previous perihelion passage this comet most probably is dynamically old.
See also Królikowska 2020.
This comet made its closest approach to the Earth on 1 May 1886 (0.198 au), that is less than two weeks before perihelion passage.
Solutions given here are based on data spanning over 0.630 yr in a range of heliocentric distances from 2.29 au through perihelion (0.642 au) to 2.00 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers small planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; these perturbations lead to escape the comet from the planetary zone on a hyperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbits).
C/1885 X1 was in the original sample of 19 comets used by Oort for his hypothesis on LPCs; however, according to presented here statistics for previous perihelion passage this comet most probably is dynamically old.
See also Królikowska 2020.
| solution description | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of observations | 217 | |
| data interval | 1885 12 01 – 1886 07 19 | |
| data type | perihelion within the observation arc (FULL) | |
| data arc selection | entire data set (STD) | |
| range of heliocentric distances | 2.29 au – 0.64 au (perihelion) – 2 au | |
| detectability of NG effects in the comet's motion | comet with determinable NG~orbit | |
| type of model of motion | GR - gravitational orbit | |
| data weighting | YES | |
| number of residuals | 392 | |
| RMS [arcseconds] | 3.92 | |
| orbit quality class | 1b | |
| next orbit statistics, both Galactic and stellar perturbations were taken into account | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| next reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | -269.67 – -255.25 – -240.74 | |
| next perihelion distance [au] | 0.894 – 0.934 – 0.975 | |
| synchronous stop epoch [Myr] | 0.989 | S |
| percentage of VCs with qnext < 10 | 100 | |
| next_g orbit statistics, here only the Galactic tide has been included | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| next reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | -269.50 – -255.09 – -240.59 | |
| next perihelion distance [au] | 1.61 – 1.72 – 1.84 | |
| synchronous stop epoch [Myr] | 1.04 | S |
| percentage of VCs with qnext < 10 | 100 | |